By Sursha Wu
At the 2025 Taipei Automation Show, the spotlight shifted from Industry 4.0 automation foundations to Industry 5.0’s focus on human–machine collaboration and sustainability. From the rise of AI Agents to advances in robotics, the message is clear: the next wave of digital transformation will drive manufacturing toward more human-centric, flexible, and value-driven smart production.
PowerArena identified 3 key trends that manufacturers should watch closely for 2025–2026.
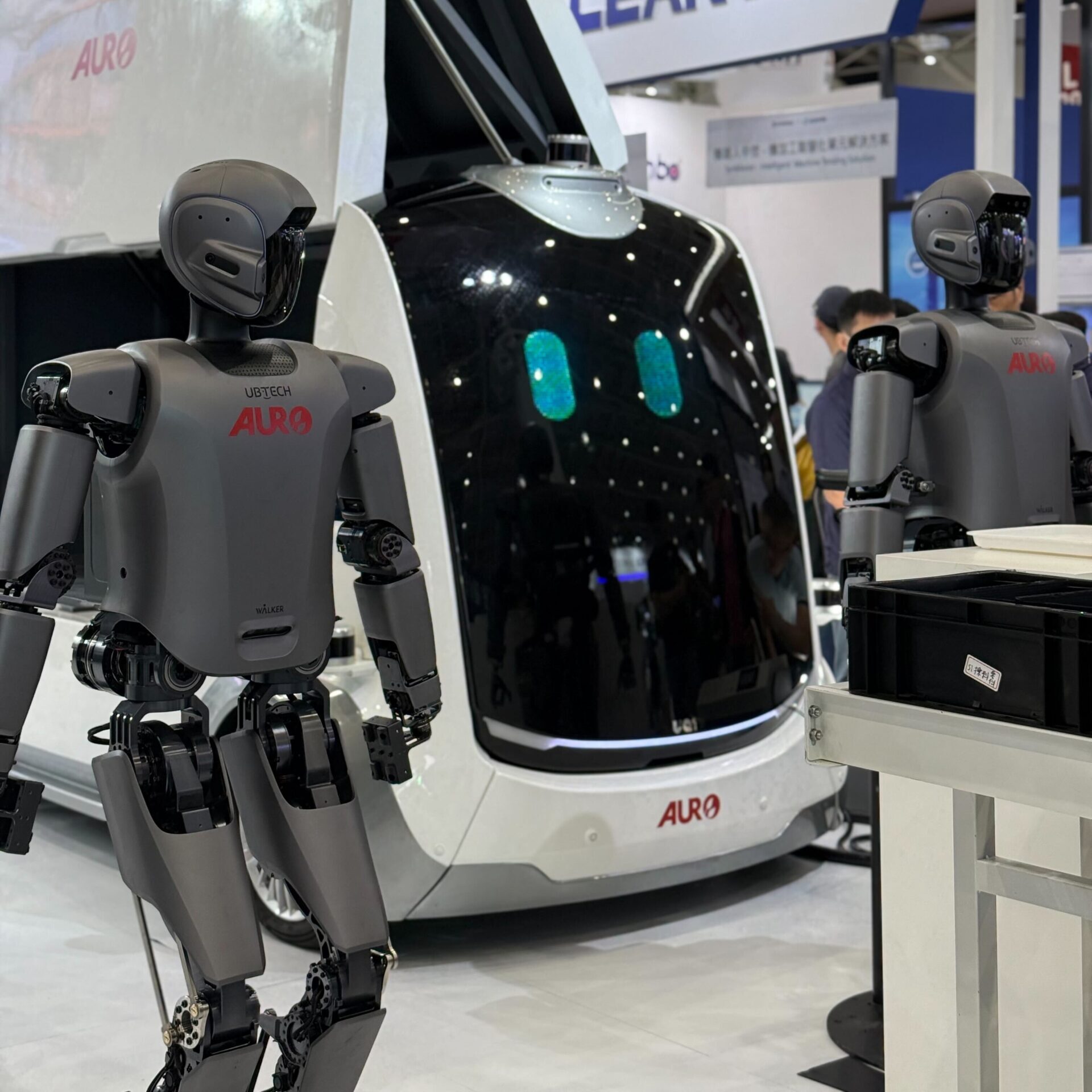
1. Humanoid Robots Entering Early Stage: Powering a New Supply Chain
The potential of the humanoid robot market is expected to be ten times that of EVs, reaching USD 26 billion by 2035 with a 37.2% CAGR.
—— Ethan Chen, Director, Digitimes
In past shows, robotic arms often “danced” to demonstrate design and motion control. This year, the trajectory is clear: industrial arms → mobile robots → humanoid robots.
The push comes largely from labor shortages and aging workforces. On shop floors, AGVs and AMRs already play critical roles in handling logistics, while humanoid robots are moving from concept demos to early trials. They are seen not only as potential factory assets but also as candidates for service applications.
For now, manufacturers lack clear, quantifiable ROI use cases for humanoid robots. Still, their development will reshape the supply chain—from motors, actuators, and control software to computing and sensors. The real challenge for manufacturers will be integrating these components into viable products that meet today’s most urgent market needs.

Techman Robot is expanding factory applications through its wheeled robots.

NEXCOM’s robots are equipped with Edge AI vision technology to meet a wider range of factory applications.
2. From Generative AI to AI Agents: Beyond Q&A in the Factory
Since 2023, Generative AI (Gen AI) has been widely adopted in customer service, marketing, knowledge management, and office automation. By 2024, it became a central theme in digital transformation.
But after two years of trials, manufacturers have realized that factories need AI models built on real-time shop floor data and domain know-how—far beyond what office use cases require.
Case Study: Compal integrates AI vision with LLMs on the production line
At the 2025 Automation Show, the shift was clear. Early 2025 discussions focused on LLMs, but this year the spotlight moved to Agentic AI (AI Agents). The driver is the factory’s growing need for data integration, deep analysis, and decision support.
Companies are no longer satisfied with AI that simply answers questions. They now expect AI to show autonomy: actively integrating data, generating insights, and providing actionable recommendations in real-world scenarios. Over time, these AI Agents are evolving into “digital employees” who is capable of accumulating knowledge and solving problems at a level that can even surpass individual workers.

The most common applications of AI Agents today are in order scheduling and production management processes, such as work order dispatching.

AI Agents / Agentic AI can help factories compare historical and real-time machine data to predict equipment lifespan and provide proactive maintenance recommendations.
Want to explore how AI Agents can optimize smart factories and manufacturing workflows?
3. OCR/AOI Defect Detection Reaches Maturity: Driven by Labor Shortages and Rising Quality Demands
AOI technology is advancing rapidly. Once focused mainly on fixed-object inspection, it can now recognize fast-moving parts on conveyors in real time and even integrate with Gen AI platforms or robotic arms, transforming inspection from a single function into a comprehensive process solution.
This evolution is powered by two forces: labor shortages and stricter quality requirements. Manufacturers now expect more from inspection tools: not only defect detection, but also data integration, faster root cause tracing, and intuitive query/analysis through AI-powered interfaces.
AOI providers are differentiating themselves in several ways:
- Low-code/no-code tools enabling non-experts to quickly set up inspection workflows.
- Multi-function integration, making AOI flexible across diverse scenarios.
With price competition reaching its limits, some vendors are targeting niche markets with specialized solutions—such as foreign-object detection in nuclear plants or defect inspection in high-temperature metalworking environments. These high-barrier applications not only deepen AOI expertise but also signal a clear trend toward specialization and integration in the market.
2025–2026 Smart Factories: Data Collection, Integration, and Risk Prediction with AI

D Forum 2025 Smart Factory Forum (Taipei Automation Show) will focus on AI data centers, cybersecurity, and the convergence of IT and OT driving smart factory transformation.
At the 2025 Taipei Automation, Digitimes hosted the Smart Factory Forum under the theme “AI²: IA × AI.
The forum highlighted the multiple challenges manufacturers now face: the AI revolution, net-zero transition, and supply chain restructuring under geopolitics.
We’ve distilled three key insights especially relevant for manufacturers in 2025–2026:
Insight 1: Data Collection — Data is Power
Comprehensive collection of production line and machine data is the foundation of manufacturing digitalization. Only with this foundation can big data and AI deep learning thrive.
—— Da-Jeng Yao, CTO, TECO
The volume and quality of data remain the foundation of all applications. Whether from machines or lines, data must be complete and accurate to hold real value. The challenge is not just capturing it, but making it meaningful, quickly interpretable, and actionable.
As Jau noted, during factory digitalization projects at ITRI, the key was not simply extracting machine data but ensuring the data supported shop floor decisions—covering people, materials, machines, and methods.
For manufacturers, the priority before adopting any AI solution should be: How do we digitize the factory and ensure full, usable data access?
Only with this foundation can more advanced predictive applications be effective.
Insight 2: Data Integration — Turning Expertise into AI
Factory data in isolation has limited value. The real challenge is integration: bridging OT and IT to form a continuous data chain that can be turned into actionable knowledge.
One of the most valuable assets here is experience. For decades, knowledge about operations, maintenance, and troubleshooting has stayed at the individual level, difficult to transfer. By capturing this know-how in digital form and feeding it into AI training datasets, manufacturers can build systems that drive management automation, quality traceability, product and equipment quality control, and production line optimization.
The ultimate goal of integration is to transform fragmented data and tacit expertise into AI-ready resources, turning AI into a shop floor advisor that supports decisions and accelerates improvement.
Insight 3: Risk Prediction — Real-Time Factory Dashboards
Factory dashboards deliver: visibility, remote plants, and training.
Once data is collected and integrated across systems, the next step is applying AI deep learning and linking with controllers or production systems to build predictive models—or even take direct action on machines and lines.
With today’s supply chain uncertainty and rising quality demands, risk prediction has become critical. Traditionally, factories relied on experience and after-the-fact reviews, often reacting too late. Now, AI enables real-time dashboards that surface anomalies in equipment, capacity gaps, or supply bottlenecks—giving management the ability to act early.
This shift from reactive response to proactive prediction is helping factories build resilience:
- Quality: Spotting abnormal trends early to prevent mass defects.
- Capacity: Using cycle-time and line-balancing data to pre-allocate resources.
- Supply Chain: Integrating logistics and material data to simulate delays or shortages.
Ultimately, all of this comes together in dashboard-based factory management. When every piece of production data is displayed in real time, managers can instantly see downtime, capacity shortfalls, or quality issues—along with the related data and potential risks.
This level of transparency and visibility shifts decision-making from after-the-fact tracking to proactive planning, enabling faster responses, better resource allocation, and prevention before problems escalate.
PowerArena provides an integrated factory dashboard that makes anomalies instantly visible, enabling production transparency and real-time response.
Want to see how AI and real-time dashboards can help your factory build resilience and manage risks?
Table of Contents